
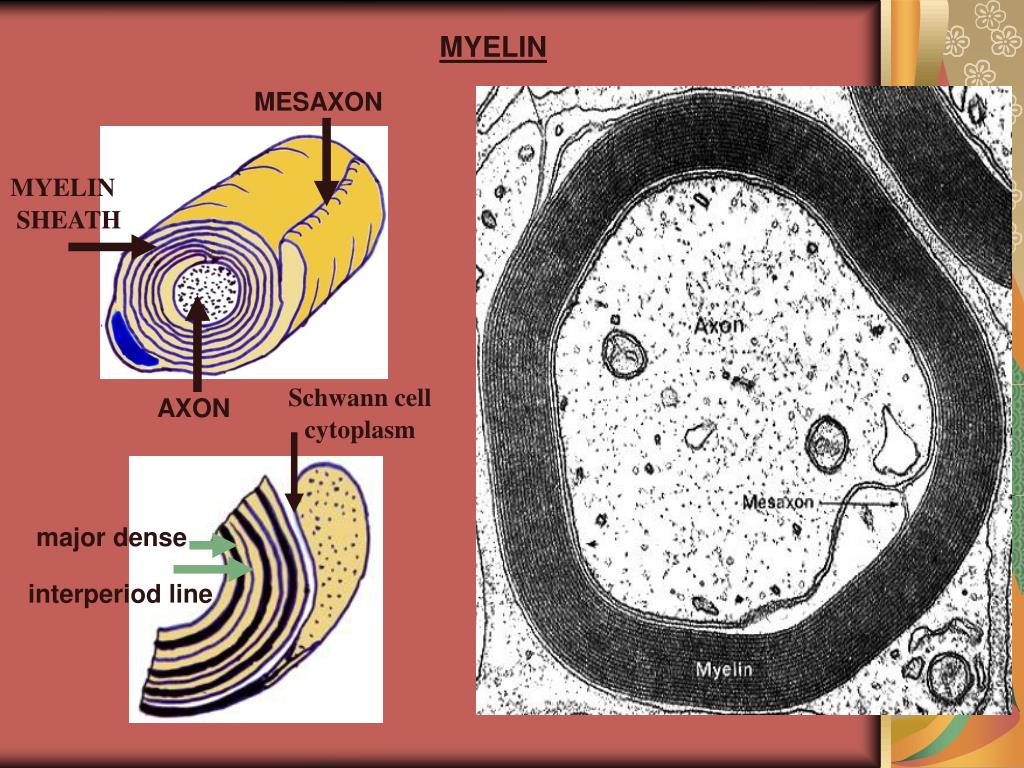
These make the axon look like a necklace of sausage-shaped beads. One extension is different from all the others, and is called the axon.
Generally, target detection can be accomplished using chromogenic or fluorescent staining. It is primarily the surfaces of the dendrites that receive chemical messages from other neurons. Immunolabeling of cells (immunocytochemistry or ICC) or tissues ( immunohistochemistry or IHC) with antibodies to study neurons is a highly utilized application in Neuroscience mainly due to the availability of a wide range of markers and the relatively low cost for performing and imaging the immunolabeled material.
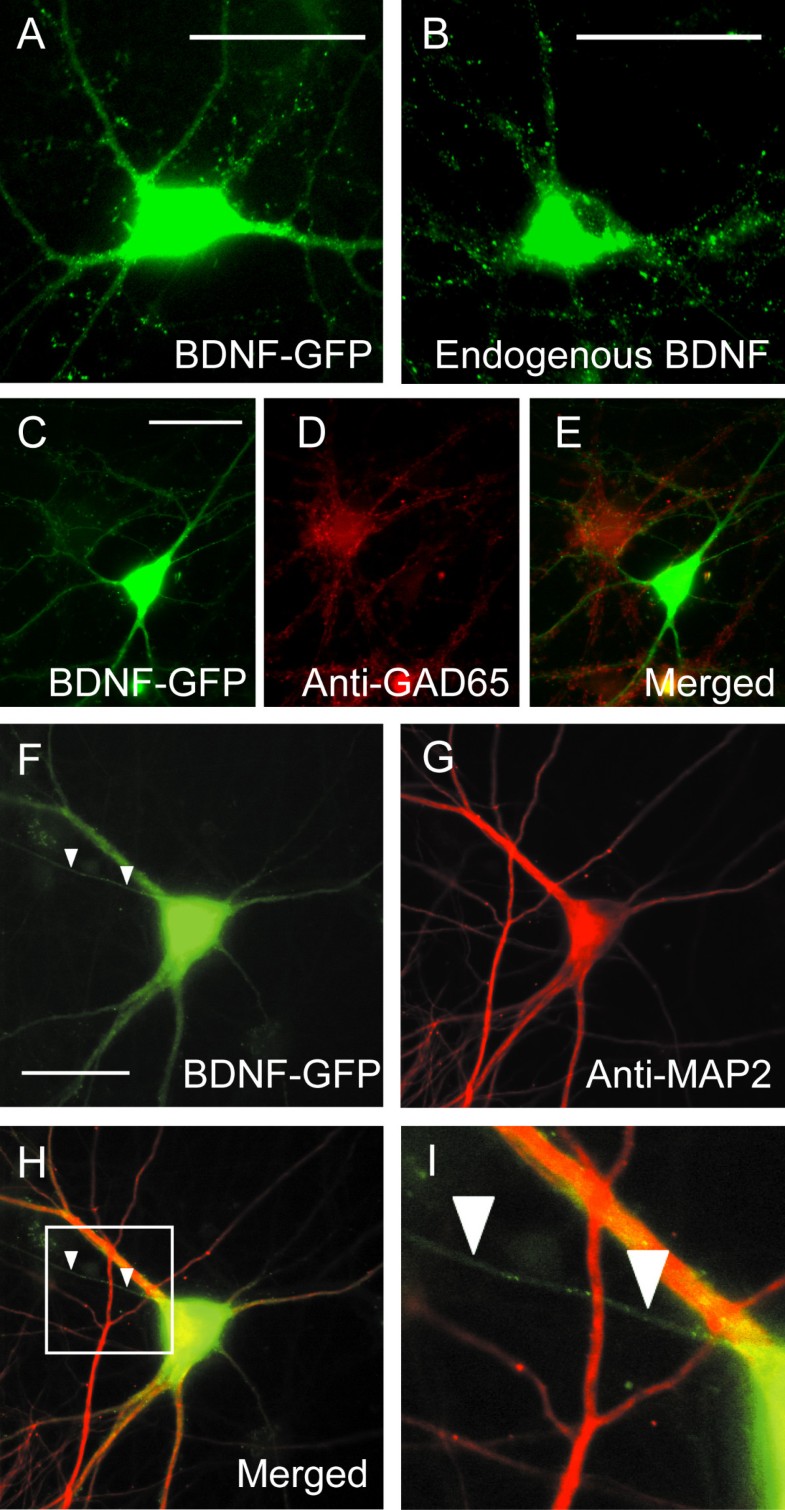
Phenotypic and morphological analysis of neurons.
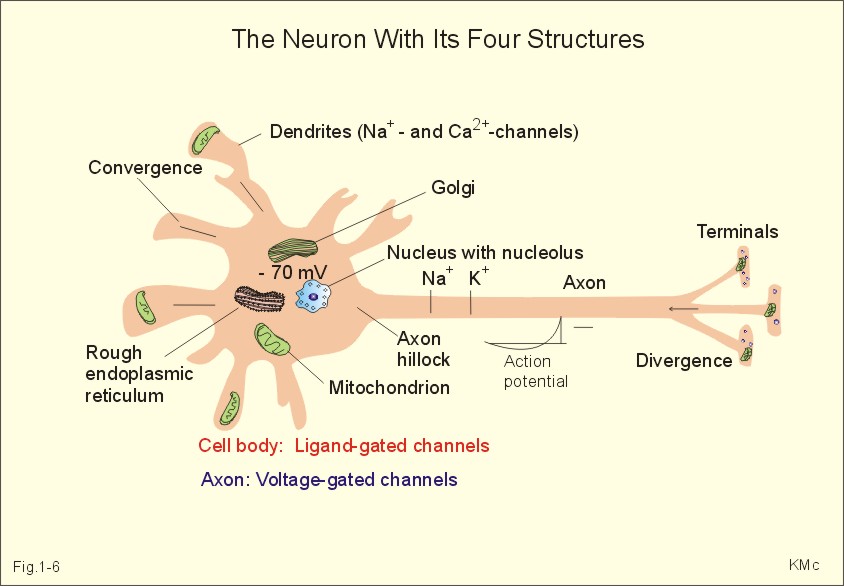
microglia, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes) Distinguishing neurons from other cell types in the nervous system (e.g.The use of antibodies for these markers in conjunction with microscopy serves as a powerful method for: These unique compartments are distinguishable using specific markers, and are generally classified into soma (cell body), axon, dendrite, and synapse. For example, most neurons fall into two main categories: spiny and aspiny. They are the chief sensors of a neuron, in the sense that the dendrites receive the incoming signals first. Creating Axon and Dendrite Traces The goal of this project is to learn all the different cell types in the brain, but we already know a lot. A neuron typically has one axon that connects it with other neurons or with muscle or gland cells.Neurons have highly compartmentalized structures that allow their distinction from other cell types in the nervous system. It is shown that dendrites have extensive connections with the axons in the form of axodendritic synapses, which form an important mode of communication between neurons (see Synapse below and Ch. What does an axon do?Īxon, also called nerve fibre, portion of a nerve cell (neuron) that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body. The structure of a neuron: The above image shows the basic structural components of an average neuron, including the dendrite, cell body, nucleus, Node of Ranvier, myelin sheath, Schwann cell, and axon terminal. A neuron has many dendrites originated from the cell body. ( sometimes arising directly from a dendrite, but generally originated from the soma or cell body). Table of Content In vertebrates, an axon, also known as a nerve fibre (or nerve fibre), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that transports. The main difference between dendrites and axon is that dendrites receive information as electrical signals with the help of small receptors present on their surface. Their presence in humans is limited, but they play an important role within. In this lecture we are going to learn about the difference between axon and dendrite, Direction of Conduction in axon and dendrite, axon and dendrite Arises and many other things. Dendrites are structures of neurons that conduct electrical impulses. If you are unsure whether or not you are looking at. Axons are structures that conduct electical impulses (messages away from the cell body. Neurons contain some specialized structures (for example, synapses) and chemicals (for example, neurotransmitters). Bipolar neurons have one axon and one dendrite extending from the cell body. Axons tend to be thinner than dendrites, which is another reason they can be more difficult to track down. Neurons communicate with each other through an electrochemical process. What is the difference between a dendrite and a neuron?ĭendrites bring electrical signals to the cell body and axons take information away from the cell body. Now, we have got the complete detailed explanation and answer for everyone, who is interested! Dendrite arise from the receiving surface of the nerve whereas axon arises from the discharging end of the nerve Dendrite is comparatively short whereas axon is comparatively long Dendrite is highly branched throughout its length while axon thickness is uniform throughout its length. This opening allows positive ions to enter the neuron and results in depolarization of the membranea decrease in the difference in voltage between the inside and outside of the neuron. This is a question our experts keep getting from time to time. Axon Vs Dendrites A Comparison Table Easy Biology Class Explain the stages of an action potential and how action potentials are propagated. What is the difference between a dendrite and an axon?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
